In the release of the Nature newspaper from 2002, a sensational statement was made: according to scientists, almost half of people who ever lived on Earth could die due to malaria. Is this disease really dangerous? In 2018, almost 230 million people were injured from malaria around the world, and about 500 thousand died as a result of infection. More than 60% of the victims had to have children under five. This is one of the oldest diseases in the world, the researchers were able to trace it at least until the time of dinosaurs. Coronavirus, Spaniard and other pandemics are simply nervously smoking on the sidelines. And although malaria learned to treat, every year in different countries there are large-scale outbreaks of the epidemic.

The situation is complicated by the fact that malaria is very easy to get infected. It is enough for a person once bitten a mosquito, which is a carrier of infection. Remember how many times the mosquitoes bite you? If you often go to the forest or to the lake, then for sure several times in one day only. Often, people do not even notice that they were bitten by the place of bite, or a characteristic scar will appear there. How can a tiny mosquito kill millions of people?
What is malaria
Malaria is an infectious disease caused by unicellular parasites, which fall into the blood of a person and destroy red blood cells. This parasite is a malaria plasmodium.There are four types of these parasites causing malaria in humans, but for most infections only two are responsible: plasmaodium Falciparum (P. Falciparum) and Plasmodium Vivax (P. Vivax).
Malarium plasmodium multiplies in two ways: it is useless inside the liver tissue and the host blood cells and sexual means inside the anofelas mosquitoes through specialized sex cells that the insect absorbs with the host blood.
How can I get infected with malaria
Malarium plasmodium can only be transmitted through the bite of the infected female of Komar Anofeles, which makes the insect vital in the chain of the disease. That is, the Komar itself is not the cause of malaria, he, rather, its carrier, but very deadly. Komarov Anofeles a lot, their bite, of course, is different from the usual mosquitoes, but it is often possible to simply not notice. As a result, malaria continues to be a common disease in those parts of the world, where this type of mosquito multiplies in large quantities, especially in the tropical regions of Africa.
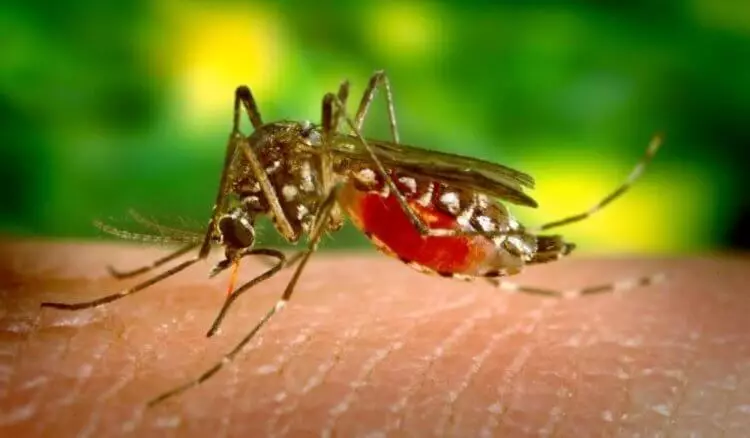
But there is a chance that the number of malaria mosquitoes will also soon increase in Russia. Here we wrote, why.
Scientists believe that malaria has had a greater impact on the migration of people than any other factor. They tried to get away from those places where the large concentrations of the aognel mosquitoes were observed. Subsequently, people came to the conclusion that the malaria mosquito cannot survive and multiply at low temperatures. With this, the movement of a person is connected closer to the north. The density of the population in tropical countries is still much less than in more northern, and the malaria played a considerable role.
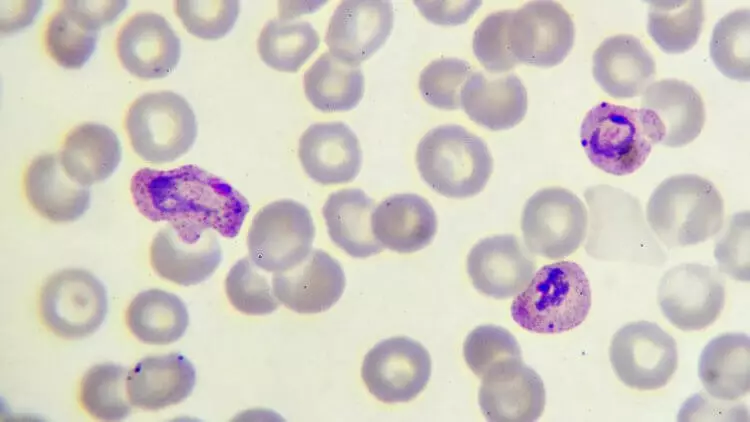
During the arid season in Africa, when there are few mosquitoes, the malarious plasmodes almost does not apply. Where is he going? Parasites are hiding in the human body, not giving infected cells to cling to blood vessels. Thus, infected cells do not fall into the blood, and the level of parasites in the body remains low, allowing the parasite to remain unnoticed. A person may not suspect that it is a possible carrier of malaria.
Symptoms of malaria
After about one or three weeks after the bite of a mosquito, anofeles and subsequent infection, a person appears symptoms resembling flu symptoms that include:
- abundant sweating;
- fever;
- headaches;
- pain in the joints;
- vomiting.
In severe cases, the skin and the eyes of the patient can be yellowed due to the violation of the liver function.
Preventive medicines or strong immunity can delay the symptoms or make them less serious. In the absence of treatment, the disease may cause complications, including difficulty breathing and weakness due to anemia, which can undergo small children and people with a weakened immunity of death risk.
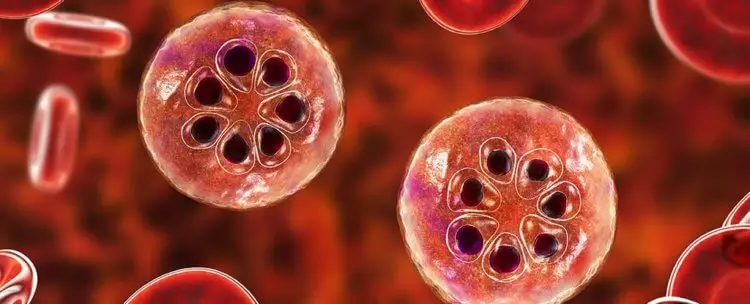
How is malaria treated?
Over time, various natural and synthetic preparations have been developed that help reduce the likelihood of infection with a malaria plasmodium. However, the legs of the medicine have side effects, the risk of complications and cause increased sensitivity to the components of the drugs.Early diagnostics gives more chances of recovery infected. Currently, treatment methods are recommended based on artemisinine anti-alarm. The combination of this medication with other drugs reduces the risk of developing stable strains of plasmodium.
Can a medicine from malaria to help from coronavirus?
One of the most common preparations against malaria is hydroxychlorookhin, which in many countries is also used to treat coronavirus infection.
Chlorochin is a widely used drug against malaria and autoimmune diseases - blocks viral infections, changing the acidity inside the cells and affects the recipes of the coronavirus of heavy acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), the outbreak of which occurred in 2003. Initially, WHO recommended him for the treatment of coronavirus, but then changed its recommendation due to a large number of eases. In addition, for many patients, hydroxychlorookhin turned out to be ineffective.
In recent years, significant progress has been made in the development of a vaccine to prevent malaria infection. In 2019, within the framework of the Vaccination Program against Malaria under the guidance of WHO in three sub-Saharan Africa, a vaccine called RTS, S / AS01 (Mosquirix trade name) was distributed, which can eliminate the malaria plasmodium, the most deadly parasite in the world.
Of course, the most effective means of combating this disease is strict control of his carrier - Komara Anofeles. The use of mosquito nets, pesticides and the destruction of colonies of mosquitoes helped many people under threat, to practically eliminate one of the oldest diseases in history.
