
Economy
The Russian economy came to the coronacrisis in excellent form, which allowed a quarantine period without special problems at the macro level, as well as financing the necessary support measures. At the same time, the Russian government operated quite restrained, which was expressed in a very moderate amount of additional budget expenditures. As a result, the budget deficit in the results of 2020 turned out to be relatively small if compared with other countries. This was also facilitated by the fact that the decline in GDP was less expectations, including due to the characteristics of the structure of the Russian economy (a relatively low share of the services sector, stronger than other quarantine restrictions) and a fairly flexible approach to the use of quarantine restrictions.
The long load increased significantly, but remained at a very low level, and the debt instruments of the Russian Federation retained the status of a protective asset among it. Some problems with servicing or repaying the debt of the Russian Federation can only be represented in the event of insurmountable technical restrictions on payments (super-sanctions), other realistic options for developing events that will lead to credit events on Russian debt in the foreseeable future, come up with very difficult.
Credit ratings from all three international agencies are at the investment level, the forecast is stable. Market risks associated with sovereign Russian duty are estimated as very low. In a sharp period of market drawdown, Russian Eurobonds were adjusted much weaker than other segments of the global market of Eurobonds of developing countries.
Corporate sector
The total volume of fiscal measures allocated by the government to combat the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 is estimated at 3.5-4.5% of GDP. The volumes are quite modest by the standards of other countries, and the support was targeted, but
Apparently, it reached certain purposes.
Restoration of prices for oil has had a positive impact on assessing the state of the economy and Russian assets. Optimism inspires the appearance of several vaccines from COVID-19.
A specific risk remains possible to strengthen the sanctuction pressure on Russia after the victory of Democrat Joe Bayden in the presidential elections in the United States. However, for a significant reaction in the market, sanctions should be very significant, which beyond the framework of personal restrictions.

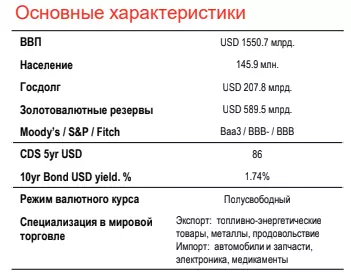
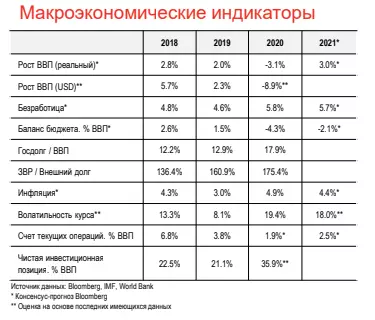
Sovereign credit metrics
Russian sovereign credit metrics even in conditions of coronacrisis do not cause any questions. The Russian government adhered to a tough fiscal and monetary policy, while maintaining an excess ruble liquidity in the banking system. Such a combination did not allow to accumulate systemic risks in the economy, and their influence on the situation during quarantine restrictions was not felt. Although the government had to seriously soften his position, increasing the cost of the budget, and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation reduced the key bid and kept it at a low level even in the conditions of accelerating inflation, these measures are not regarded as a change in the main approach to fiscal and monetary policy.
Forecast of the change of sovereign credit metrics: Positive
• As a result of 2020, the budget deficit is modest than other developing countries (see 3)
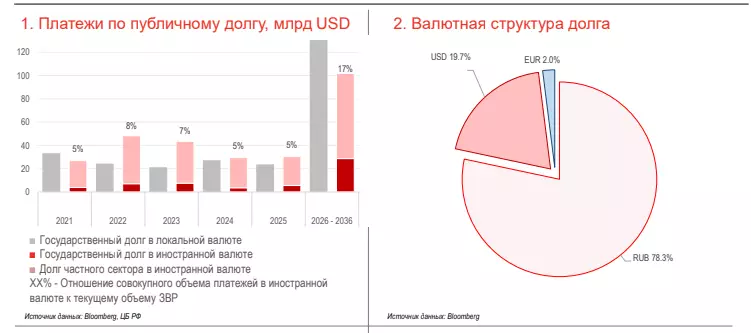
• Long load in relation to GDP approached 18% is a very low value. The main source of financing of deficit - ruble debt (OFZ), and the lion's share in 2020 was redeemed by residents. The placement of sovereign debt obligations in foreign currency was episodic.
• The debt currency structure continues to shift towards an increase in the share of ruble liabilities, their share has increased to 78.3% (cm, 2). The size of sovereign currency debt relative to GDP is only 3.5% - very low levels of developing countries.
• Payment schedule is extremely comfortable, all sovereign and even corporate currency obligations are covered with foreign exchange reserves (see 1)
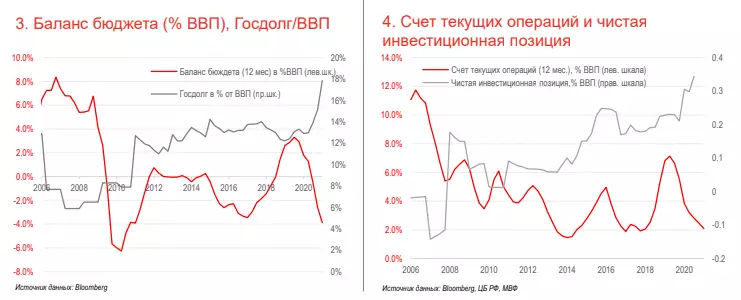
• The current operations account in 2020 decreased, but the main reason was the low prices for oil and obligations assumed under OPEC + to reduce production.
Banking and corporate sector
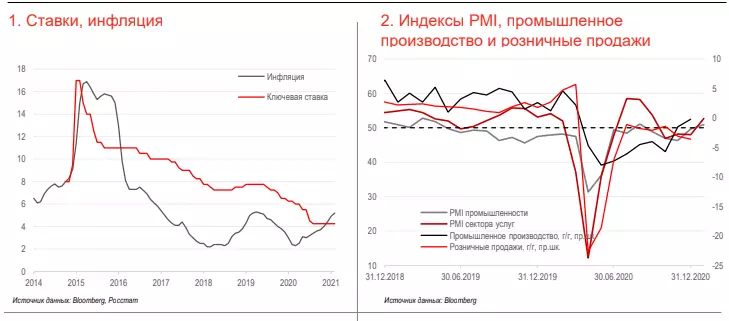
• The Central Bank of the Russian Federation since July 2019 began to systematically reduce the key rate from 7.75% against the background of reduction of inflation risks, and the events of the spring of last year were forced to act more aggressively. At the July meeting, the key rate was reduced to 4.25%, after which the regulator took a pause against the background of some acceleration of inflation. According to the results of 2020, the key rate was below inflation for the first time since 2014 (see 1).
• The PMI processing industry index is slightly lower than 50 points, approximately there, where it was before the coronacrisis. Industrial production itself, as, however, and retail sales were restored only partially. However, taking into account the reduction of stiffness of restrictions, the gradual restoration of business activity is expected (see 2).
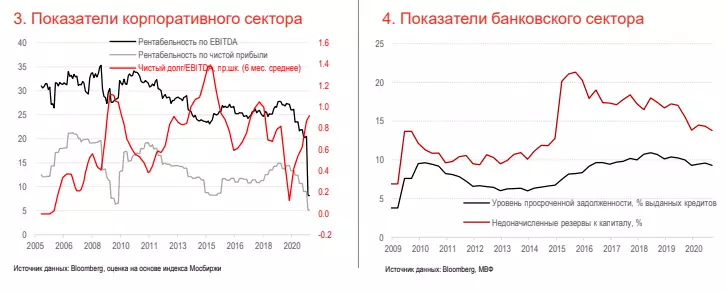
• The ratio of net debt of companies to EBITDA is below 1X, which indicates a low level of debt burden, even despite some growth in 2020, with the stability of the banking sector and the normal development of the situation in the risk of serious problems with the debt as a whole, the economy remains low (See 3).
• The banking sector is quite pricked. The capital adequacy ratio is 12.7% in September 2020, which is a very comfortable value (the minimum safe level of Basel-III is considered to be 10.5%).
• The level of problem loans for the banking sector of Russia is growing and is at the level of 9.3%, which is a high level of emerging markets, but rather low value for the last 5 years. The amount of imputed reserves is about 13.8% of the capital, which involves a limited negative impact on the capital of banks with a substantial write-off of problem debt (see 4).
Forecast of changes in credit metrics in the corporate and banking sectors: stable.
Read Original Articles on: Investing.com
