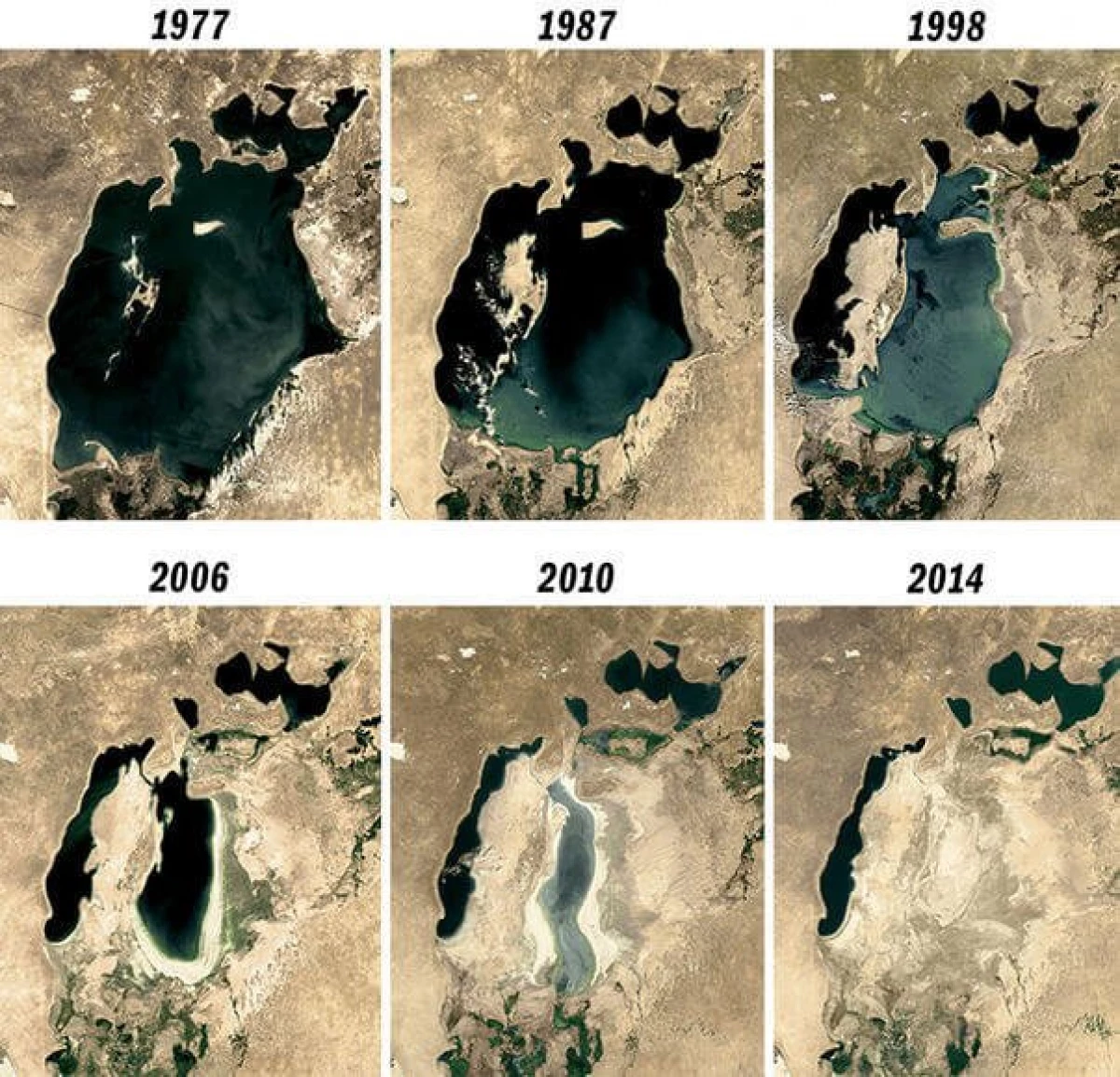
One of the largest ecological catastrophes of the 20th century was the practical disappearance of the Aral Sea. It seemed that quite recently, fishermen in Central Asia went to the flight for half a year - in the mid-1960s on the border of Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan held the coastline of one of the largest lakes in the world - the Aral Sea. Today there is a desert and a constant environmental disaster zone. Unfortunately, in the future, a similar fate can overtake the largest water-closed planet, which, because of its impressive sizes, can be classified both as a sea and as a faceless lake. The water level in the Caspian Sea, located at the junction of Europe and Asia, according to scientists forecasts, to 9-18 meters away by 2100, which will entail large-scale environmental consequences. And if for a catastrophe, comprehended by the Aral Sea, the political leaders are responsible, the reason for the evaporation of water in the Caspian region is to change the climate.
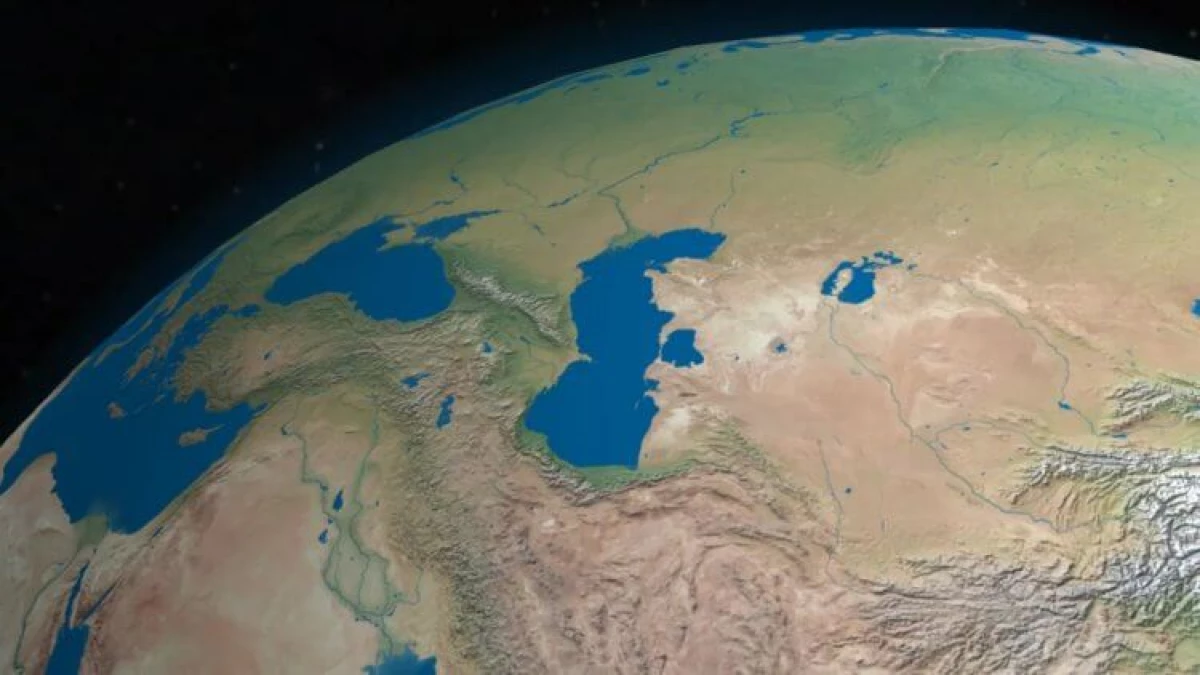

What happens to the Caspian Sea?
The likelihood that in the XXI century the world can lose the Caspian Sea, high. Recently, in the magazine Communications Earth And Environment, a work was published, according to which the Caspian, separating the boundaries of Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Iran, may lose to a third of its surface. In fact, the loss of water in the Caspian Sea occurs since the 1970s, but the team of Dutch and German researchers proved that the Caspian drying rate accelerated to six or seven centimeters per year and in the coming decades will continue to gain the pace.
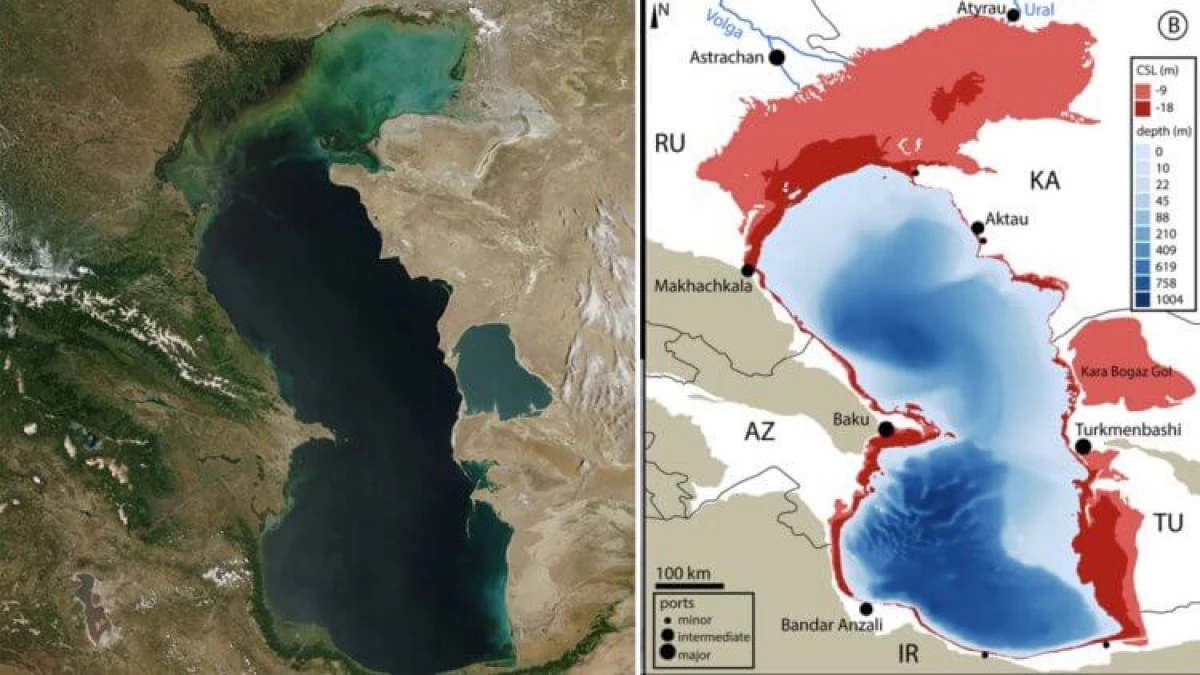
In the geographical understanding of Caspian - not the sea, and the largest lake in the world is an area of 371 thousand square kilometers. By the end of the XXI century, its area will decrease into the territory, commensurate with Portugal, which threatens the extinction of unique species of animals that live only in this region.
The researchers also argue that the welfare of the Caspian Sea today depends on the three main factors. The first is the contribution of the Volga River, which provides 90% of the water volume of the Caspian Sea; The second is the winter amount of precipitation, and the change in temperature on Earth and evaporation of water is the third and most important. According to the data obtained, despite the fact that winter precipitation in the northern part of the Volga basin will become more and more stock river and its reset to the Caspian Sea can incorrect in the future, the effect of evaporation of the lake will lead to a predicted reduction in the sea level.
It would seem to be a paradoxical phenomenon: while the global temperature rise is the reason for increasing the oceans, the water level of the seas and huge lakes will decrease due to the same effect of increasing temperature. As a result of the changes occurring, Baku will not be the port, the Bay of Kara-Bog gall will disappear, and in the northern part of the sea the water will free the huge land of land.
See also: What happens to the oceans of the earth?
The consequences of evaporation of the Caspian Sea
It is noteworthy that the authors of the study do not consider a catastrophe that occurred with the Aral Sea and what the Caspian expects in the XXI century, the events commensurate. So, by 2003 the volume of water in Aral was about 10%, and its surface area is about a quarter from the initial one. The coastline was 100 km away, and the salinity of water increased two and a half times. So, today there is a sand-salt desert of Aralkum on site at the place of the real sea.

In the case of the Caspian Sea, the situation is different - the water in it will still remain. Even according to the gloomy scenario, the Caspian may save up to 66% of its area with a depth of 1000 meters. However, the loss of one third of the square can turn the Caspian to the most present, from a biological point of view, the Dead Sea. The cause of the death of living organisms will be the low level of oxygen.
Want to always be aware of the latest news from the world of science and high technology? Subscribe to our news channel in Telegram so as not to miss anything interesting!
"At first it will not have a lot of importance for deeper areas, but ultimately decline in the sea level can cause an ignition (lack of oxygen) in seabed depths," a geologist warns from the University of Utrecht (Netherlands) and the Frank Sviseling collaborator, What is the Spanish EL PAIS reports. Less than the amount of ice and the oxygen contained in it, the excessive concentration of nutrients in rivers and the increase in global temperature, "create ideal conditions in order to deeper the deeper Caspian oxygen levels (already low), thereby destroying all life," say Authors of scientific work.
