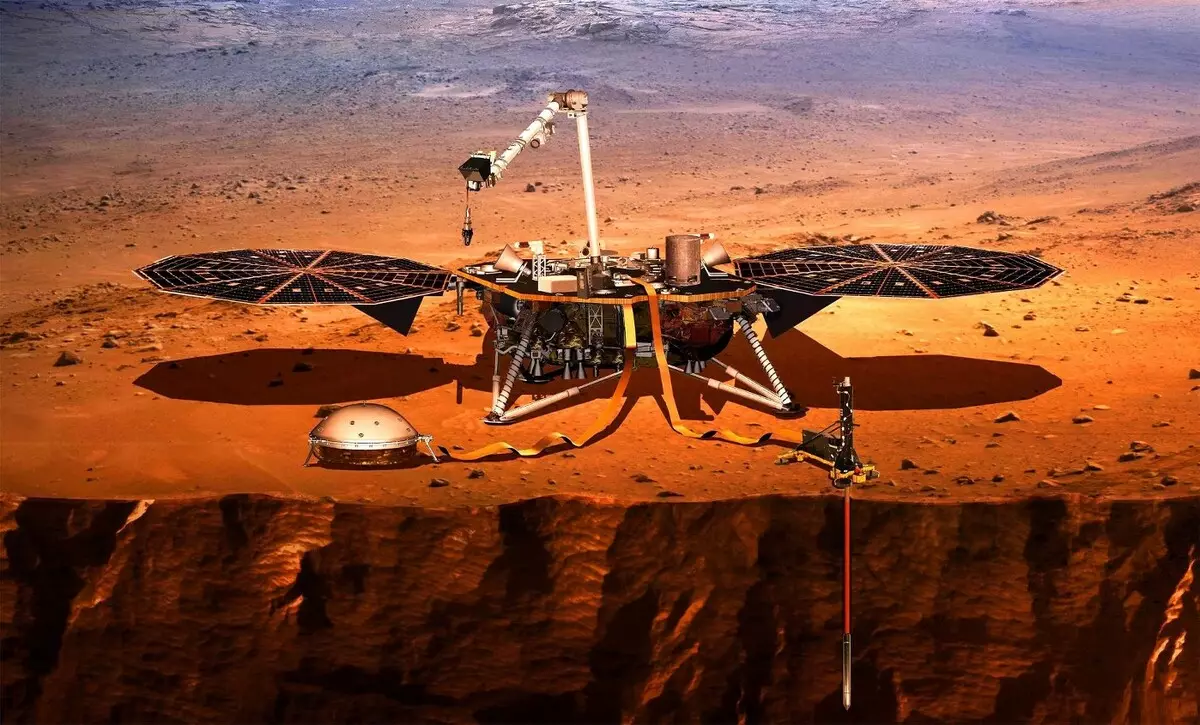
Using the data that was collected by the NASA Insight spacecraft, the international group of researchers calculated the size of the Mars kernel. The results of the work are the subject of discussion of the 52nd Lunar and Planetary Scientific Conference, which this year is held in online mode.
In accordance with modern models, the inner structure of Mars is represented by the bark, mantle and the core. The average thickness of the bark is about 50 km (maximum - up to 125 km). It takes 4.4% of the entire planet.
The mantle consists of the upper, middle and pre-lower parts. Compared to the earth, it is characterized by a smaller pressure range due to such strong gravity. Minerals and silicates, for example, grenades, olivine and pyroxes, isolated in the mantle.
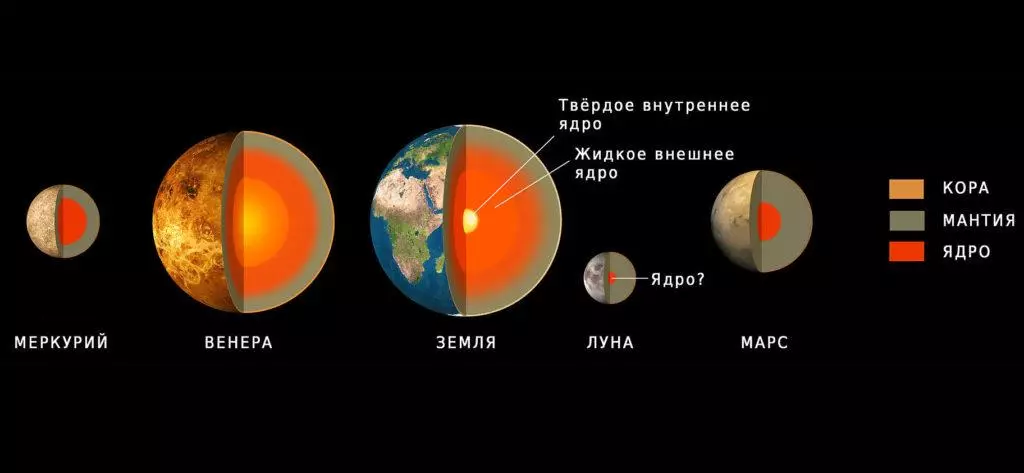
According to scientists, the kernel is completely or partially in a liquid state. It is present in its composition predominantly iron with an admixture of sulfur, nickel and hydrogen. Previously, it was possible to measure the size of the nuclei of only land and the moon. For this, the researchers used seismic data.
The essence of the method is to track earthquakes. With the help of special sensors, the sounds emanating during underground jolts and oscillations are collected. To measure the size of the Mars kernel in the same way, NASA has launched the Insight mission back in 2018. Its main task was to delivery to the surface of the red planet of the planting apparatus with a seismometer on board.
Insight scientific purposes in the field of geological evolution of Mars:
- measurement of size, composition, aggregate kernel state;
- definition of structure, thickness, composition of the bark and mantle;
- Measurement of the temperature of the internal layers of the planet.
The device landed not far from the equator of the planet. From this point on, the observation of "marceings" began. Since 2018, the sensors have recorded about 500 soles and registered the corresponding amount of seismic data. In comparison with the earthquakes of oscillation of the surface of Mars, in most cases weaker.
Also among them there are about 50 jackets with magnitude 2-4 (Richter scale provides indicators from 1 to 9.5). These oscillations turned out to be sufficiently strong in order to be used to measure the internal characteristics of the planet. Previously, precisely thanks to INSIGHT data, scientists have established an approximate depth and thickness of the layers of the Mars's bark.

Seismographic sensors capture a lot of indicators, on the basis of which experts can calculate the size of the internal structural parts of the planetary body. For example, they fixes, at what depth, waves arising due to an earthquake begins and end. This is how time calculations are made, which was required for the passage of the wave through the or another region of the planet.
Next, the density of the layers is established and, finally, the depth of the boundaries between the core and the mantle in different parts of the planet is determined. All of these data allowed us to calculate that the radius of the nucleus is within 1810-1860 km - it is about half of the size of the earth's core.
The results of the study were unexpected for scientists, since it was previously believed that it was much larger. Also the density of the central part of the planet is about 6700 kg / m3. The set radius gives reason to believe that the kernel is more lungs than expected.
Channel site: https://kipmu.ru/. Subscribe, put heart, leave comments!
