When there are no intermediaries in the transaction, any participant may deceive the other. In the blockchain, the problem is solved using strict mathematical algorithms for which blocks are created.
In the material we will tell you who creates and checks the blocks in the blockchain. You will learn how the consensus algorithms ensure the security of this process.
- P2P: where peer networks are used
- Encryption in the blockchain: on the fingers
- Blockchalter - chain of transaction blocks. We disassemble the definition according to
- Encryption in the blockchain: why do you need a digital signature
- Principle of operation of the blockchain: who creates blocks
- For what purposes and tasks fits the blockcha
Remember basic concepts
- A peer network is a network in which the nodes interact with each other without a mediator.
- Blockchain is a kind of peer-to-peer networks, a chain of transaction blocks.
- Block - special structure for recording transactions.
- Transaction - an entry on changes in the state of assets.
Distrust in the blockchain
Since there is no server in the blockchain, add and verify information to users themselves. At the same time, each participant may chase his personal interests to the damage to the security of the blockchain. From here there is a problem of distrust of the participants to each other. To solve it, mathematical algorithms are used, which will be discussed further.Imagine that there are assets on your wallet, and another blockchain user believes that they are not. Without outside interference, it is difficult to decide which of two rights. It is necessary to choose among users of those who will check the transactions and add only the correct. Such users are called miners.
Mainers - Blocked participants who are engaged in the creation of new blocks and transaction checks.
To organize the proper operation of miners, it is necessary to agree, who will be and how they will perform their work. This is a difficult task, because you need to come up with such rules, which will be more profitable to observe the miners than to break. This is a classic example of a task from the game theory: how to choose a strategy that will be the same advantageous for participants with different interests.
Such a task was formulated and solved by mathematicians in the last century. Now this solution provides security both in the blockchain and in other complex technologies. To understand how Mainers manage not to violate the interests of each other, consider this task more.
The task of Byzantine generals
In the 1982 scientific article, a logical dilemma was formulated. It illustrates the problem of communicating nodes of a peer-to-peer network that negotiate the next step. As an analogy, Byzantium was used - an ancient feudal state with a multitude of independent armies. Hence the name - the task of Byzantine generals.
The action takes place during the siege of the city of the Byzantine army. At night, legions from different sides surrounded the city. The generals of each legion are waiting for the order of the commander-in-chief. Order options: "attack" or "retreat".
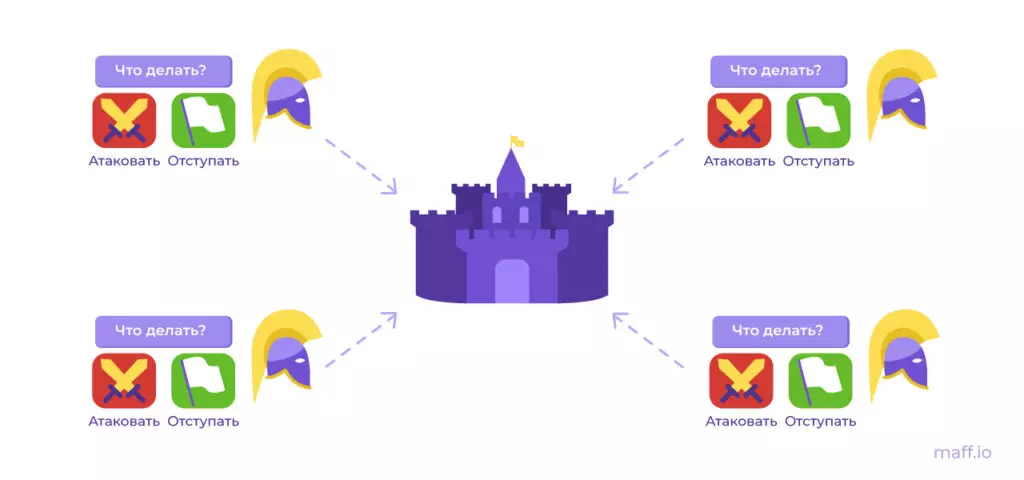
The first complexity of the task - the Empire is in decline. Any of the generals and even the commander-in-chief can be traitors of Byzantium interested in defeat. Generals need to be considered to not allow unfavorable outcome. In total, three outcome of the battle:
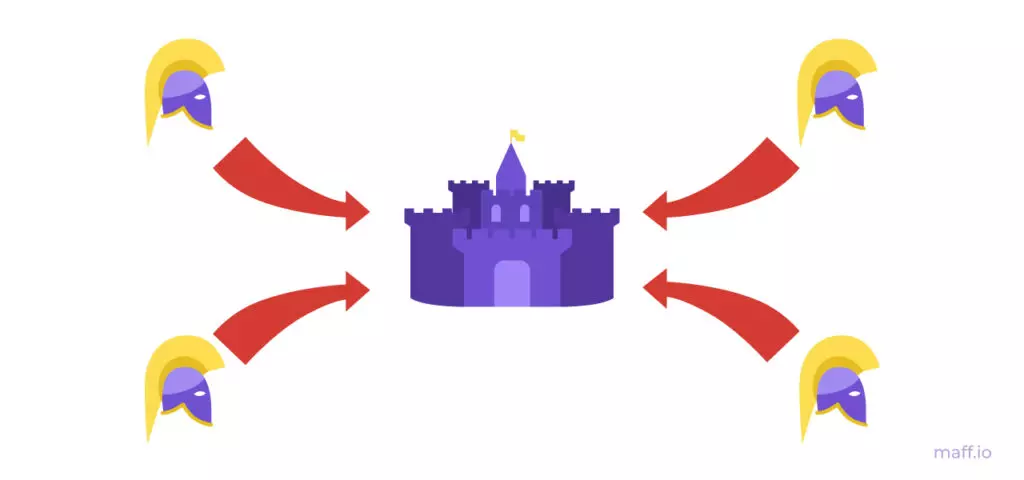
Favorable outcome. If all generals attack - Byzantium destroy the enemy.
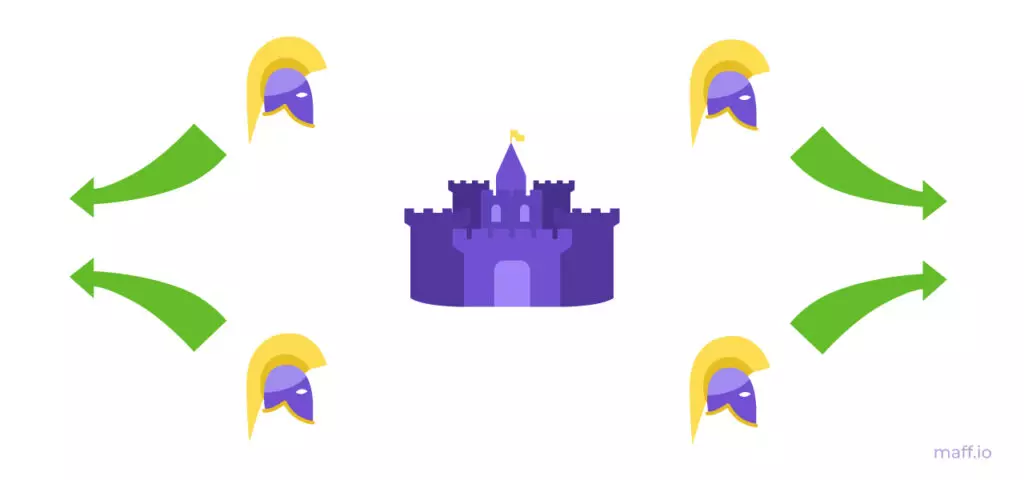
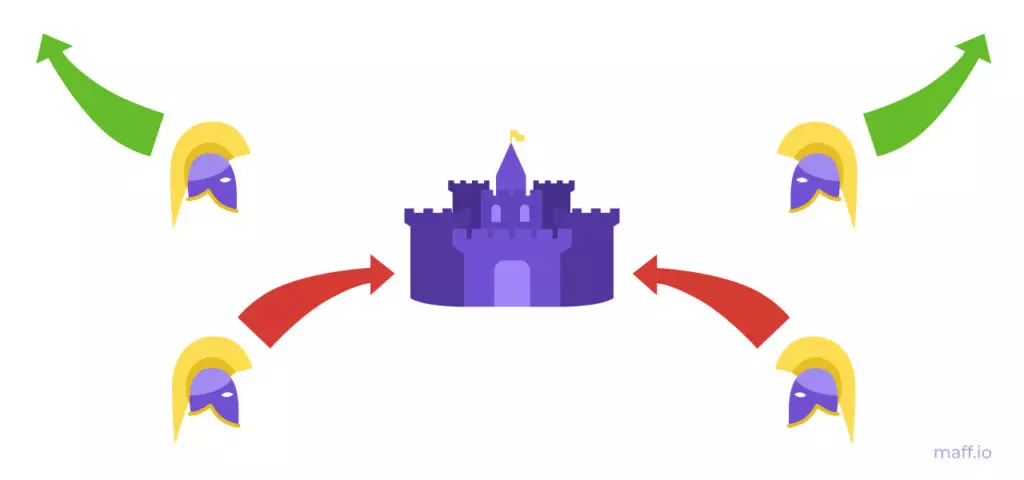
Intermediate outcome. If all generals will retreat - Byzantia will retain their army.

An unfavorable outcome. If some generals are attacked, and some will retreat - the enemy eventually destroys the entire Army of Byzantium in parts.
If each general will act at its discretion, then the likelihood of a favorable outcome is quite low. Therefore, the generals need to exchange information among themselves to come to a single solution.
The second complexity in the task is the lack of a reliable communication channel between generals. Even if there are no traitors among generals, the information may be false. For example, the courier will delay or captures. This situation will confuse other generals and an incorrect decision will be made. In such conditions, you need to develop a unified strategy of actions that will be advantageous for all generals.
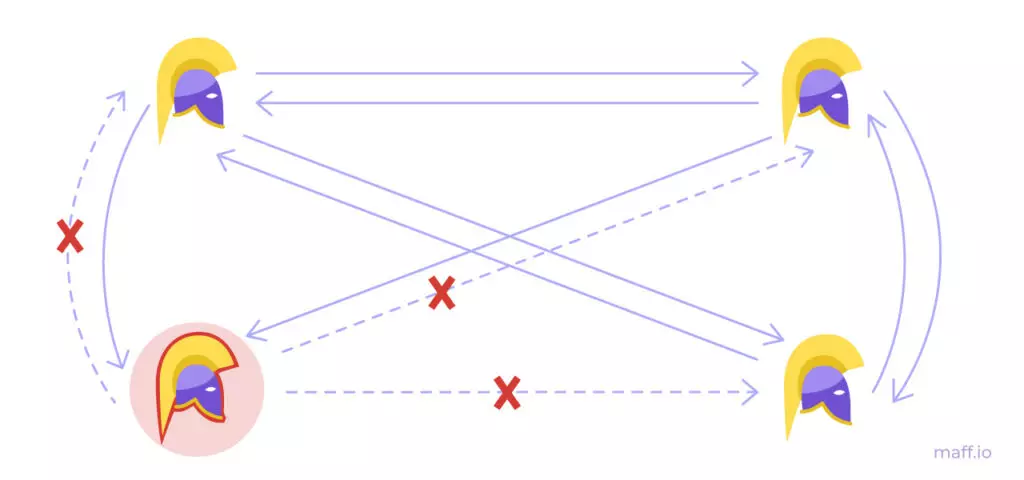
Mathematics proved that it is always possible to obtain a solution in this task, if the correct generals are more than two thirds of the total. In different systems, the task can be solved in different ways.
Byzantine fault tolerance - the ability of the network to continue to work, even if some of the nodes refused or act maliciously. In other words, this property of the network in which the task of Byzantine Generals has been solved.
Byzantine fault tolerance is necessary in the systems of aircraft engines, at nuclear power plants and practically in any system, the actions of which depend on the results of the work of a large number of sensors. Even Spacex considers it as a potential requirement for its systems.
If this task is to apply to the context of the blockchain, then the generals are miners. They must agree and recognize the transaction to real so that it fell into the blockchain. This process is called consensus.
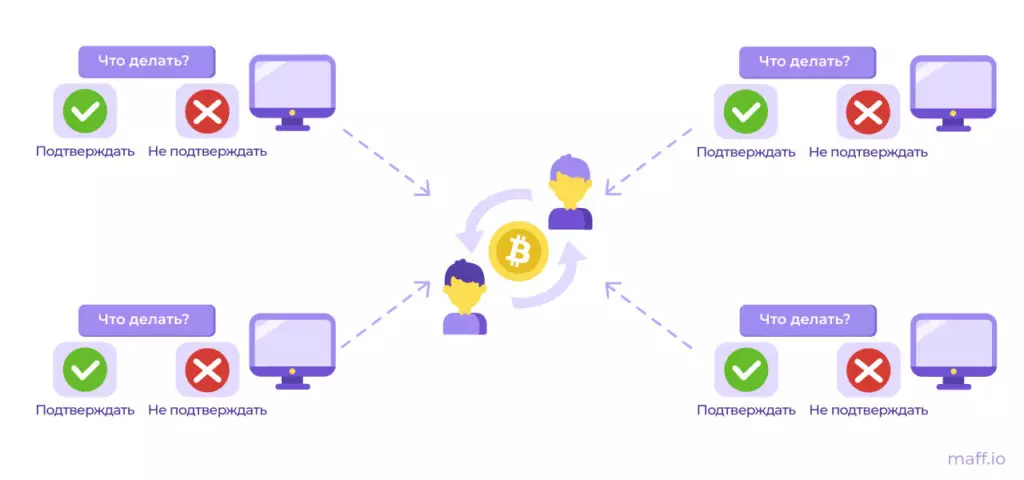
For example, miners see that one user wants to send bitcoins to another. The first Mainer believes that such a transaction must be approved. The second suspects that this operation produces an attacker. The third disconnected from the network and did not check the transaction. Take a single solution and then come to consensus.
Since the task of Byzantine Generals has several solutions, then different blocks achieve the Byzantine fault tolerance using different consensus algorithms. Consider more the most common.
Algorithms consensus
The blockchain works on the basis of a distributed network. There is no single center that manages this network. To organize the safe operation of the blockchain, you must negotiate who will be miner and how it will create blocks. Mainers work on strictly defined rules called consensus algorithm.
The consensus algorithm is a method that describes how Mainer is selected in the blockchain and by which rules it creates blocks.
To better understand what a consensus is needed in the blockchain system, imagine the tenants of an apartment building. The blockchas them are needed to interact with each other and make decisions on the development of the house: collect money for overhaul, choose servicing organization or appoint duty. There are three ways to negotiate - three different consensus algorithms. Each of them is based on a certain mathematical model.
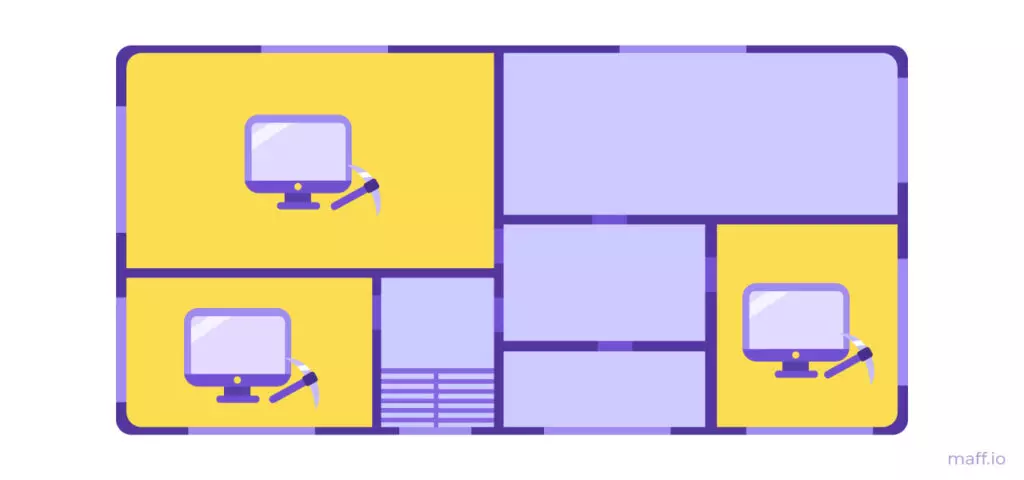
Proof of Work (POW) is an algorithm for evidence of work. Mainer can become any vest at home. To create new blocks, it will have to use his computer to solve complex cryptographic tasks.
The algorithm will consider the correct version of the blockchain one in which the most blocks. And the most of the entire blocks will be in the version, to the creation of which the tenants spent most of the entire computer capacities. A very democratic method is obtained: if 51% of miners believe that transactions in blocks are correct and will be. Therefore, the blockchain is almost impossible to hack.
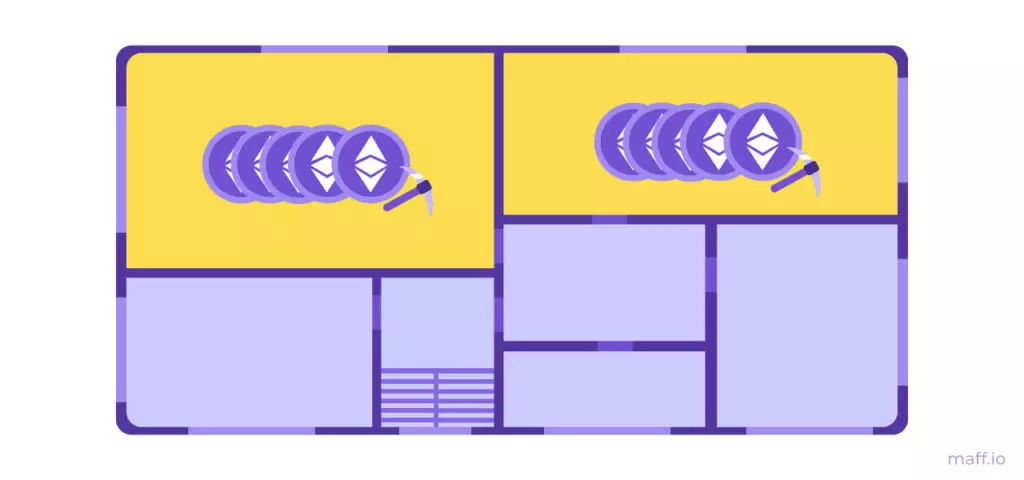
Proof of Stake (POS) is an algorithm for the proven share of ownership. Mainers become those who have more assets in the blockchain. We will have this tenants with the largest apartments. And in the Etheric Blockchalter, for example, it will be users who have the most cryptocurrency ETH. With this algorithm, electricity costs are minimal, since the creation of blocks in the blockchain no longer requires solving complex cryptographic tasks. The more your share in the blockchain, the more often you will create new blocks.
The right version of the blockchain, as in Proof of Work, will be considered the one in which the most blocks. But Proof of Stake cannot be called democratic. Most of the blocks will create not most residents, but the richest tenants. However, it is even safer. If Majnem belongs to most of the house, then it will be becoming malicious to happen.
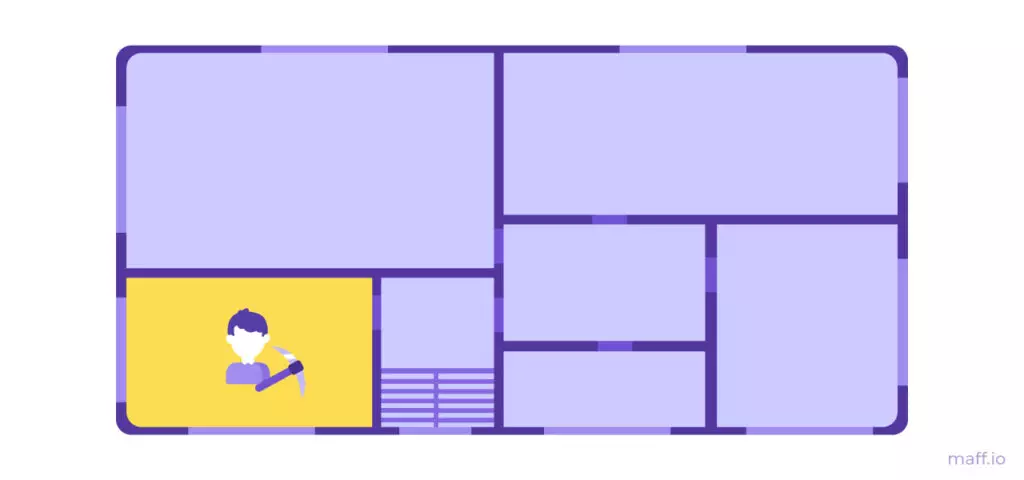
PROF OF AUTHORITY (POA) is an algorithm of personality proof. It may be that the tenants gathered and decided that there will be one apartment to create blocks. This algorithm is distributed in private, closed blocks. For example, it is well suited for managing an apartment home from our example.
The elected miner itself chooses the true version of the blockchain. He will have to identify himself so that all residents believe him. If at some point the tenants will cease to be consonants with the maneer solutions, they will be able to assign another. The new Mainer will begin to build its chain of blocks, and the old blockchain will exist separately. Such a process in the blockchain is called Hardforka.
Consensus algorithms are a lot. Constantly invent new, but these three are the most well-known, time-tested and frequently used.
Conclusion
In any peer-to-peer networks there is distrust between the participants. In the blockchain, miners solve this problem. These are the users who check the transactions and add only correct to new blocks.
The 1982 article describes the task of Byzantine Generals. It was first described in the algorithm of how the network can continue to work, even if some of the nodes were denied or inflicted maliciously.
In the blockchain, three varieties of consensus algorithms are used:
- Proof of Work (POW) is an algorithm for evidence of work.
- Proof of Stake (POS) is an algorithm for the proven share of ownership.
- PROF OF AUTHORITY (POA) is an algorithm of personality proof.
