Acetate - ethanol metabolite, which is produced by the Aldh2 enzyme. It interacts with gamma-amine oil acid (gamc) - the brake neuromediator of the central nervous system. He is responsible for how the drunk man behaves. For example, people who bloom from alcohol are observed Aldh2 deficiency. So they cannot quickly produce acetate.
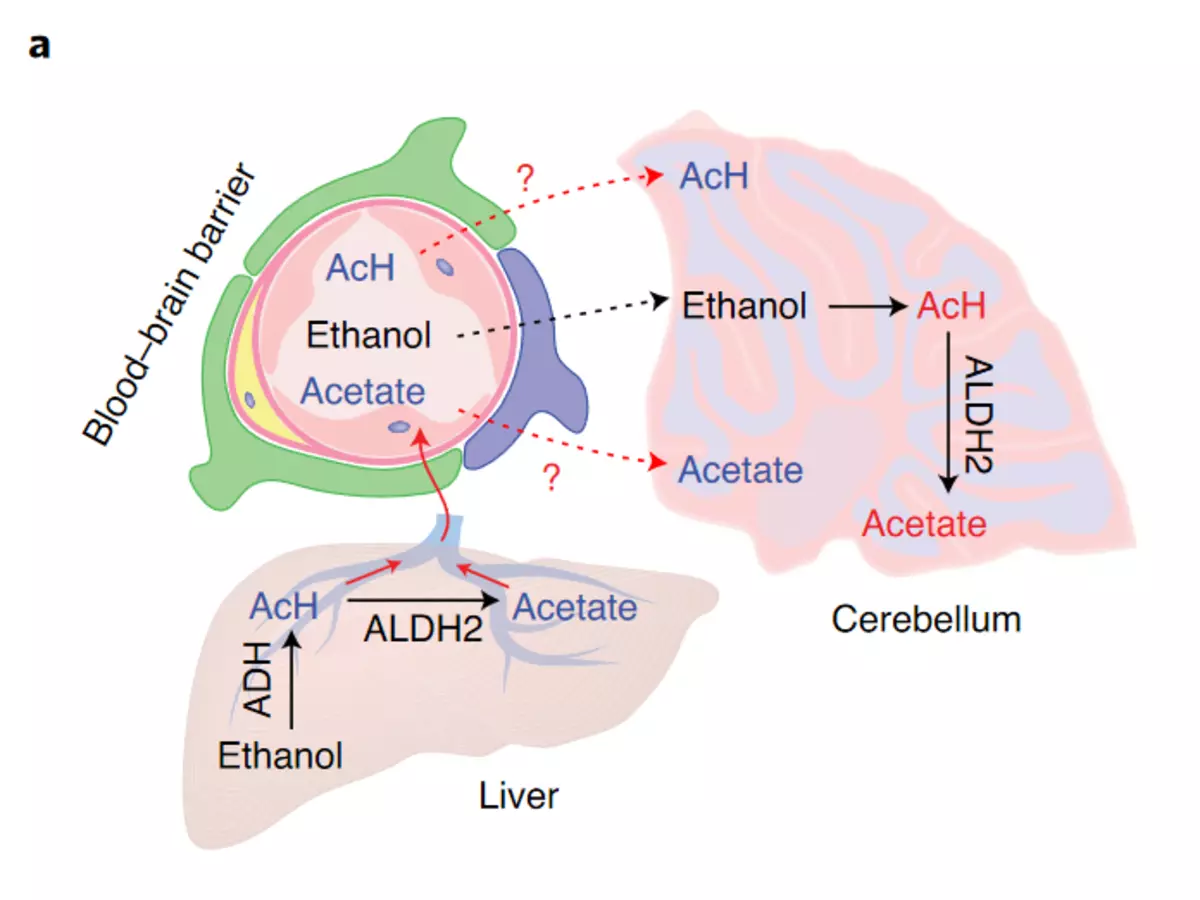
Earlier it was believed that ethanol metabolism occurs in the liver, and there were already decay products to the brain. However, a group of American neurobologists from the Institute for Alcoholism National Institutes of US health found that the oxidation of acetate can occur in the brain. It turned out, it is expressed in cerebellum astrocytes and causes coordination loss. Details of the opening are published in the journal Nature Metabolism.
Scientists investigated the expression of the MRNA ALDH2 in various areas of the brain at 11 sections of the mouse brain tissues and three sections of the human brain tissues. It turned out that the most expression is expressed in cerebellum, and the least in the prefrontal crust.
Also, the team conducted an experiment on mice. For this, scientists brought rodents, in whose brain was not an aldh2 enzyme. Then they and ordinary animals were given a small amount of ethanol (one gram per kilogram of weight). During the analysis, it turned out that the alcohol stimulates the appearance of acetate in the cerebellum. However, the derived mice turned out to be more resistant to the effects of alcohol, since the enzyme almost did not turn alcohol into acetate, which accumulated in the brain. In rodents without astrocytic Aldh2, there was also a lower level of gamke in the brain after alcohol consumption. Hence the best coordination.
In mice with a shortage of the enzyme in the liver, such a dependence was observed. This allowed the authors of the study to assume that the source of acetate in the cerebellum - alcohol, and not aldehyde. But it still has to prove.
Finally, scientists came to the conclusion that the Aldh2 enzyme, located in the liver and the brain, affects the body in different ways. They intend to continue the study of this enzyme in humans. Also, experts called an astrocitary Aldh2 an important target for the treatment of alcohol addiction and neurological diseases.
Source: Naked Science
