Investments, especially in the stock market, may seem too complicated to take them on their own. In fact, everyone may understand them, you just need to carefully examine the details.
"Take and do" tells where to start investing - from the purpose of the goal and the choice of instruments before drawing up the plan and the first actions.
1. Put the goal
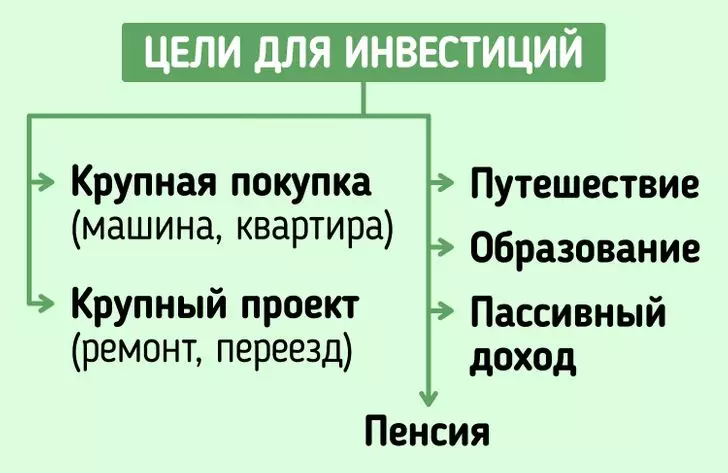
Any investment should have a goal. Without it, high risk of breaking and spend accumulation on the first attractive thing. Here are examples of goals that can be selected for future investments:
- Large purchase (apartment, house, car, machinery);
- large project (repair, moving to another city or country);
- journey;
- education;
- passive income;
- pension.
2. Get rid of large debts
If you have loans with a percentage rate higher than the estimated profitability of investments, first close them. Otherwise, you will remain in the minus, because interest on debts will ease capital gains from investment.
3. Form the Financial Reserve
Financial reserve is a stock of money for emergency situations like loss of work, sudden health problems, breakdowns of large equipment, etc. Reserve will help hold out as long as possible until the problem is solved. For example, before receiving the work and the first salary in a new place. Ideally, the financial reserve should be enough for 3-6 months of life without income. Investments without financial reserves are associated with risk. At the first emergency it will have to sell assets. Because of this, we can lose part of their value, if at the time of sale assets asked for money.
4. Select the investment tool

- Deposits. They are considered a safe investment, since the cost of money is usually stable even taking into account inflation. To protect the accumulation from it and increase the capital slightly, invest in savings accounts with interest payments.
- The property. Typically, investors buy it for resale or renting. The first allows you to make a profit from the difference between buying and selling, and the second is regular income. However, it should be borne in mind that investments in real estate require significant time costs and greater initial capital.
- Other physical assets. These include cars, artwork, collectibles, precious stones and metals.
- Stock. Buying shares, you become the owner of a part of the company that released them. Shares can grow or fall in price, and then the financial result of the investment will be the difference between the purchase and sale price. In addition, the company can share part of the profit and pay dividends to shareholders.
- Bonds. Buying a bond, you give a duty to face that has released a valuable paper. They can be private companies, municipal districts or state. The market price for bonds changes in the same way as on stocks, so the investor can earn on the difference between the purchase and sale price. In addition, the bond issuer pays interest at the rate specified in the security prospectus. Usually twice a year.
- Funds. These are private organizations that collect ready-made securities portfolios: shares, bonds, etc. Buying part of the Foundation, you acquire a piece of the investment portfolio in the hope of growing its total cost. Funds can help you assemble a balanced securities portfolio without having to buy each separately and follow the price dynamics.
To invest in the last three asset you will need to open a brokerage account.
5. Examine the selected tool
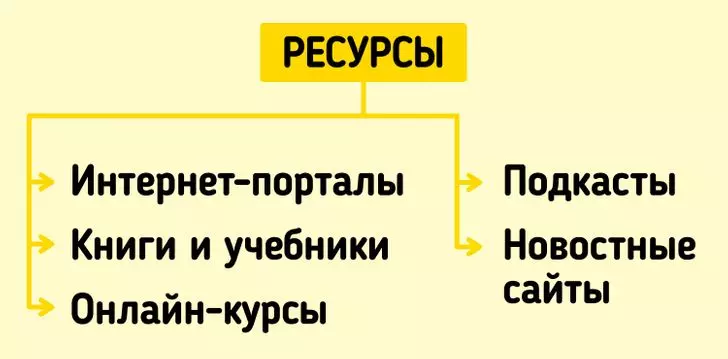
Each investment tool has its own nuances. Examine them before investing. As sources of information fit:
- specialized Internet portals for beginner investors;
- Books and textbooks (for example, the famous bestseller Benjamin Graham "Reasonable Investor");
- online courses from the largest brokers or Internet sites (for example, EDX or Coursera);
- investment podcasts;
- The sites of news agencies where you can follow the latest events in the world of finance.
6. Find out what investments differ from speculation
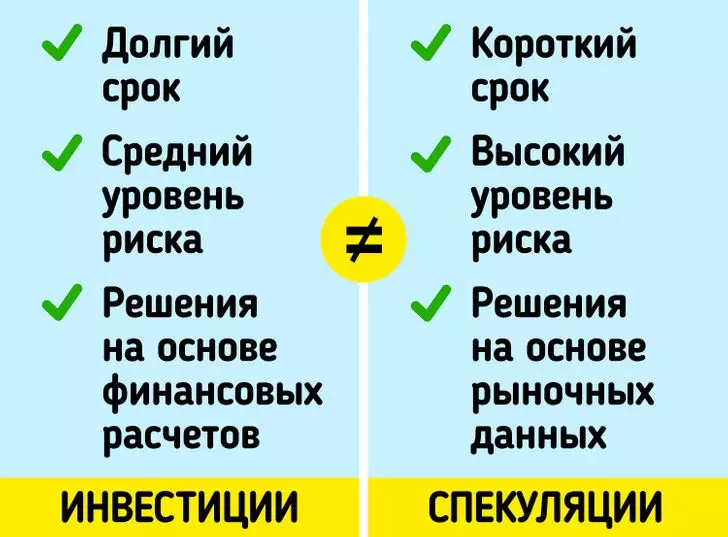
Investments are financial assets or physical items that are acquired to obtain additional income or increase the cost in the future. A speculation is a financial purchase and sale operation. It is associated with a significant risk of loss of all cost, but at the same time with the expectation of significant benefits. For investment is characteristic:
- long time planning horizon;
- average risk level;
- Decisions based on payments and financial indicators.
Specs are distinguished:
- a short period between buying and selling an asset;
- high risk levels;
- Solutions based on technical data (for example, a chart of the value of shares), market psychology and personal opinion of speculat.
Speculations carry a high risk of capital loss, so they should be careful and not to be confused with investments.
7. Make a plan and start investing
- Determine the budget. Consider how much you can allocate for investment. This can be a one-time contribution (for example, if you want to invest your savings) or monthly. In the latter case, it is recommended to allocate for investments up to 20% of the monthly earnings. If it seems too big digit, just postpone how much you comfortably now, and in time, increase the amount.
- Install the Deadline. Determine the period for which you invest money. It depends on your purpose. Some are long-term character (for example, apartment and pension), others are short-term (travel and repair).
- The degree of participation in investments. Think how active participation you are willing to take into drawing up your portfolio. Investors are divided into active (they themselves pick up the tools, actively follow the dynamics of their price and pay a lot of time) and passive (prefer to invest in the funds, where the finished portfolio is already assembled).
- Risk. It is important to remember that investments in any tools are conjugate with risk. Therefore, invest only those money that you will not need in a few months. Also define what kind of drawing of the portfolio you are ready to accept, and which is not. Depending on the degree of risk, choose more conservative investment instruments for the portfolio (deposits, bonds) or, on the contrary, aggressive (shares).
